The world-medium cannot be an empty space
 Terms are used here that are explained in the page
Matrix
Terms are used here that are explained in the page
Matrix
Space arises from relationships between local places. However, relationship arises by the medium.
A medium that governs all aspects of our physical world has been a centuries-old goal of physics. Until this medium is recognized, our physical world consists of separate particles whose distances are considered as empty space. The question of one medium for particles and another for space makes no sense. Time and force remain unexplained if their effect continues to be viewed as a tunneling through absolute emptiness. In my paper "The Matrix," a theory is presented that explains a medium for distance-time-force as the basis of all physical events.
This matrix is a network of relationships of all distances resulting from oscillations in the elasticity of scaled fields down to zero. Through this scaling, the smaller scales become the medium of the larger ones. This is not a circular argument, but rather the generalization of the medium, which scales on itself down to zero distance. The field oscillations in the medium thus generate a zero time and, taking the Planck factor into account, an infinite force. Thus, the ranges of distances, times, and forces are defined from zero to infinity by this medium. The structure of this medium is referred to here as a Matrix.
 The
basic idea was to find a spatial structure in which all values in terms
of time and energy are scalable.
The
basic idea was to find a spatial structure in which all values in terms
of time and energy are scalable.
The solution was found in a spatial structure of tetrahedra, elements consisting of 4 centers or 4 parities of a spatial oscillation.
Space: Take a plastic bag with glass balls, connect their centers and you will see a hexagonal structure made up of tetrahedrons.
Time: The resulting equal distances are divided by a medium-speed and so receive a time unit.
Force: The elasticity with which the original state of harmony is restored creates the impulse. With the unit time measure we get the frequency. Impulse x frequency creates the energy.
 Until then, it sounds embarrassingly easy. However, it is only the tip of
the iceberg. This is about a geometry that also includes time and force.
Therefore, my paper “The Matrix” must always be consulted. It is all about a
double oscillation in 4 dimensions, where push/pull can be found in the
known 3 dimensions and time in the 4th dimension.
Until then, it sounds embarrassingly easy. However, it is only the tip of
the iceberg. This is about a geometry that also includes time and force.
Therefore, my paper “The Matrix” must always be consulted. It is all about a
double oscillation in 4 dimensions, where push/pull can be found in the
known 3 dimensions and time in the 4th dimension.
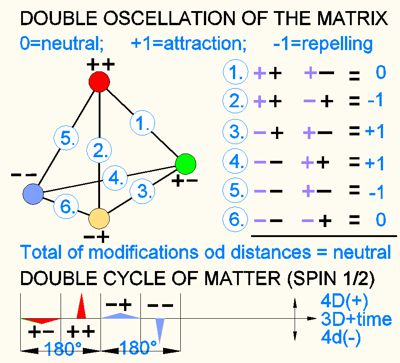 How should a double oscillation be imagined? While pressure/tension in
the three spatial dimensions visible to us can be imagined as a wave-like
deformation (sine function), the wave function from an invisible fourth
dimension is only recognizable as a point-like pulsation. These interactions
result in the following constellations of moments:
How should a double oscillation be imagined? While pressure/tension in
the three spatial dimensions visible to us can be imagined as a wave-like
deformation (sine function), the wave function from an invisible fourth
dimension is only recognizable as a point-like pulsation. These interactions
result in the following constellations of moments:
(++) is an oscillation
moment (red), where 4D moment and 3D wave is at (+) as maximum.
(+-)
is the moment or parity (yellow), where 4D (+) parity is zero and the 3D
(-) parity is max .
(-+) is the parity (green), where the 4D (-) parity is
max and 3D (+) parity is at max.
(- -) is the parity (blue), where the 4D
(+) parity is at zero and 3D (-) parity is at max.
While the 3D impulse
(parity) directly alternates the field density, the 4D impulse alternates it
as a secondary effect by the internal property of the vibration-center (point location).
The upper image shows the parities, the lower image shows the effect as spatial density or reduction / enlargement of the point distances. While the 3D momentum (parity) directly alters the field density, the 4D momentum alters it as a secondary effect of the internal properties of the respective oscillation center (point location). As a primary effect, the 4D moments always create a compression of 3D space (gravity).
As a double oscillation, physics explains the entire cycle as 360°, with the 180° cycle being interpreted as charge + (90°) - (90°). The other part of the cycle, 360-760°, is attributed to antimatter, which also has charge as parity. Unfortunately, in old physics, matter and antimatter are considered a completely separate thing, which in matrix theory is seen as just the reverse side of one and the same particle. Consequently, the cycle of a particle from the 3rd dimension is 760°, but from the 4th dimension it is 360°, which was then interpreted as 1/2 SPIN in 3D. In short: in 3D, it has 2 cycles while in 4D it has one cycle. See https://www.michaelis.ch/matrix-2-e.html#spin-e
 The field oscillations described here applys to so-called "EMPTY" space.
Particles are created when this space (as a tetrahedral space) collapses
repectiv
its four colors are > zero. The collapse migrates into the space between
as an octahedron, which then takes on an existence in "empty space." Here,
the tetrahedra are shown in yellow and the octahedra in purple.
The field oscillations described here applys to so-called "EMPTY" space.
Particles are created when this space (as a tetrahedral space) collapses
repectiv
its four colors are > zero. The collapse migrates into the space between
as an octahedron, which then takes on an existence in "empty space." Here,
the tetrahedra are shown in yellow and the octahedra in purple.
The double oscillation
produces 4 parities:
++ +-
-+ - - .
these are the 4 parities that add up to zero in every tetrahedron at every
sequence. So the
tetrahedron is the true unit of this matrix. The intervening octahedra (as a
result by the arrangement of these tetrahedra) consist
entirely by parities of surrounding tetrahedra. The medium of these
tetrahedra and octahedra are just the smaller scales of the same matrix.
Consult here
space is
oscillation oscillations (oscillation in a oscillating medium).
The double oscillation has a cycle of 720°. How can this be imagined?
A guitar gives us an example. As the 4D coordinate to 3D, the string is perpendicular to the
sound body. The string has a cycle (left/right) of two parities. During
right parity, a maximum tension is created in the sound body. During the
zero position of the vibrating string, a minimum tension is created in the
sound body. At left parity of the string, a maximum tension is created in
the sound body, the same as at right parity. Thus, measuring devices would
measure a left/right sine wave on the string, while they would measure two
sine waves in the sound body ((+) to zero). Since the sound body
symbolizes the visible 3D space, the matrix speaks of a 720° cycle. In
physics, however, it has become common practice to only speak of a 360°
cycle, whereby the particles (the measurement on the string) are therefore
only regarded as 180° or 1/2 SPIN, while bosons and photons are attributed
to 1 SPIN (1 and -).
The matrix-geometry of "EMPTY" space
 pix
1
pix
1
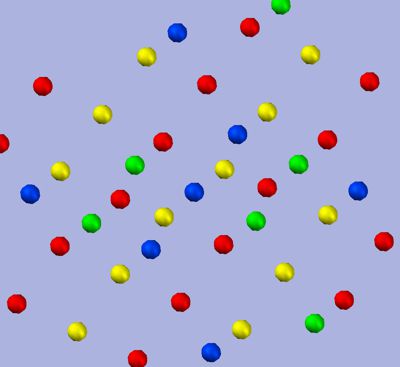
Theoretically, dimension null is considered the basis of all geometry. The simplest representation of space, with its scales, point relationships, distortions, density, size, etc., is a point space. It is represented here in a plane, but its point-relationships could be strings, areas, and volumes. It could also be oscillating cycles of dimension 4 and higher (as pulsating points).
 pix
2
pix
2
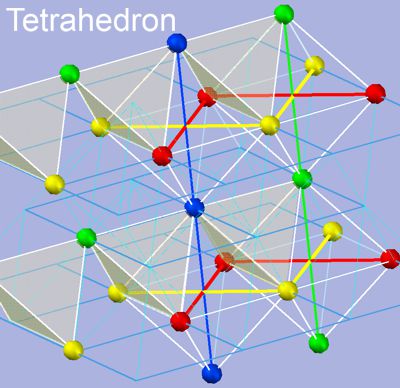
The image shows the relationships of the colored points, such that four points with 4 colors form a tetrahedron. They display 4 parities by 4 colors. These are the four parities of a 4D cycle, as described above. It shows both hexametric and orthogonal relationship structures. For simplicity, only some of the tetrahedra have been shown. When the entire space is filled with tetrahedra, the space reaches its theoretically tidest density.
Here's the proof: Fill a plastic bag with equally sized glass spheres, connect their centers, and you'll find the hexametric structure of tetrahedral space. It's the densest packing of space with equal-sized fields, whose centers are the four parities of a four-dimensional oscillation.
 pix
3
pix
3
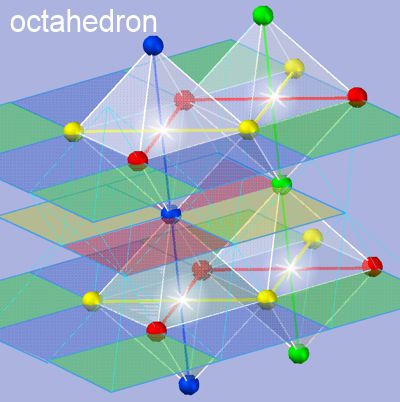
The image shows the octahedra as the spaces (gaps) between the tetrahedra. An
octahedron has only three colors at its vertices. This results in a moment
inside the octahedron froy the missing color (colors here are parities,
which only form an equilibrium when four colors are combined). In the
image, the checkerboard-like colored areas symbolically represent the change
in the vibrational parity of the moment or the missing color in the
octahedron. The light in the center of the octahedron indicates the location
of this momentum. It is a potential that arises only in the octahedron
during collapse and by the double oscillation (see
the space is Oszillation)
.
It is the mass carrying Fermion.
The diagonals of the octahedra symbolically represent the three forces. They form the three simultanious relationships, which theoretically extend to the end of the world (or rather, of its observation) and are the basis of a reference effect free of V=c (entanglement). At CERN, they are interpreted as quarks. See my chapter LHC-firewerks in my main Page.
One wonders what medium serves the internal forces in an octahedron. Herein lies another secret of matrix space. Any violation of the equilibrium (moments as 1-dimensional strings) is again based on the 1/3^x smaller scale. The space's medium is space by the matrix structure reduced by 1/3^x. This consists, as far as can be seen here, of four dimensions, which, due to our lack of understanding, are perceived as 3D + time, but are actually a polydimensional simultaneity.
The matrix-geometry of Tetrahedron, Octahedron and Cube
How are the basic types of tetrahedrons and octahedrons distributed in space? This is a purely geometric comparison, even distances in the Matrix space are also frequency and energy.
 pix
4
pix
4
Visible here is a cube, 2 nested tetrahedrons with an intersection in
form of an octahedron and the residual forms a; b; c to fill up the cube.
For the sake of math, a cube with side lengths √2 has been assumed, thereby
producing interior distances of hexagonal directions of 1. We see that a
central octahedron has a tetrahedron (green and magenta) on all 8 sides. We
recognize that the parts (a) above (c) below and the parts (b) on the 4
edges are required to fill this structure into a cube. With a little
imagination we see that the parts a; b; c are always ¼ octahedron in size.
If the space were filled with cubes, then the ¼ octahedron with the
adjoining neighboring cubes would again produce whole octahedrons on each
side length and edge. Now the only question that remains is What is the
volume of a tetrahedron.
This we finde out :
[Cube (√2)^3] - [4·a] - [4·b] - [4·c] - [1·octahedron] = 8·tetrahedra.
Because of [4·a];[4·b];[4·c] will become [1·octahedron], the cube will have
4 octahedra and 8
tetrahedra. Becaus all internal parts of a cube are =1 , it derives:
Volume (octahedron) = 1^2·(√2)/3 = √2/3 = 0.4714; 4·octahedra = 1.8856
Vol.(cube) = (√2)^3 = 2.8284
Vol.(tetrahedron) = (cube) 2.8284 – (octahedron) 1.8856 = (tetrahedron) 0.9428
1·tetrahedron=0.9428 / 8 = 0.1178 = 1·"part" a; b; c; = (octahedron) 0.4714 / 4 = 0.1178
Here we recognize the mystical volume.relation. It is equality of tetrahedra and
"parts" a; b; c; .
Although mathematics based on a subvolume of 0.1178 and an orthogonal spatial structure would be possible, this makes no sense in quantum terms. The energies of 3D space, with their point distances (the λ of the wave quantities), are assumed to be unity 1.
 pix
5
pix
5
Due
to the fact that the orthogonal space cannot add up to zero per tetrahedron
units, its cube units never become transparent. It would be an opaque space.
Nevertheless, it is latently present as an orthogonal view in a hexagonal
space, but energetically shows no effect. It consists of octahedra, but
these are energetically = zero, since all corners of the octahedron do not
belong to it, but to the surrounding tetrahedra. However, we recognize an
orthogonal space structure based on (√2) in the central octahedron with its
diagonals. This will be also explained as QUARKS in my paper
the LHC-Fireworks
(LHC = Large Hadron Collider)
The Matrix structure in multi dimensions
 Pix
6
Pix
6
The medium of the matrix is a structure of always equal distances. The
rule
the densest filling with spheres
is the appropriate algorithm for 3D. However, the principle applies to all
dimensions. In D1, it results in a circle, in D2 the circular area, in D3
the sphere, and in D4 a sphere with a 4D distance as its radius. In this
sense, the line (D1) is divided into equal distances (d=r▪π), D2 into areas
(F=r^2▪π), 3D into spheres (V=4/3▪π▪r3), and in D4 into spheres of (V4D =
2▪r^4▪π^2▪1/4 ).
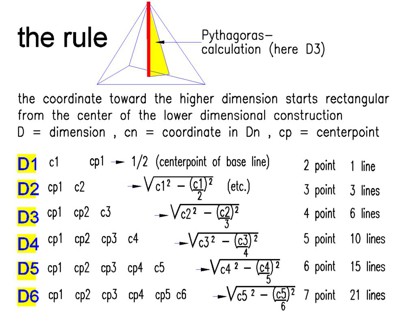
The algorithm for positioning the next higher coordinate is as follows:
From
the center of the element in the lower dimension (e.g. x/y), perpendicular
to the higher dimension (e.g. z), and shortened by the hexametric factor as
Pythagoras calculation,
this yields the value of the next dimension (e.g. z).
Pix 6 shows an octahedron (white) with
8 tetrahedra (marked as Merkaba here in red) and the corresponding parafield (black). It shows the 3
axes of the culminating parities (energy lines) in blue, red, and yellow.
The perpendicular starting point of the 4D coordinate is at the center of
the tetrahedra (yellow). From there, the four vertices of the tetrahedra are initiated as
four parities and as simultaneity. These four parities culminate in zero,
the normal state of empty space. If there is an excess of energy, this
energy will be released at the center of an octahedron (shown here in white), and a proton
will be created.
More about this in
the particle
on my main page.
 pix 7
pix 7
The image section at the top left shows the geometric construction of a 4D starting point. The center of the 4 triangular faces (green dots) connected to the opposite corner results in the volume center of the tetrahedron, which serves as the starting point of the 4D coordinate. The image shows all other volume centers of the tetrahedra (here as yellow spheres). These can be connected with 4 indigo-blue lines that create a cube-like space of equal distances.
We must realize that the matrix of n-dimensional space is not an academic game.
It is the result of the first rule: the densest filling of space with
fields of equal size. This is followed by Max Planck's rule that distance
equals energy density. This requires a dependent scale, as equilibrium, in
the sense that the distance between field centers, a ratio of 3^n field
sizes to the next scale, again generates fields of equal value that have the same
center. All of these rules allow the matrix to be mathematically described
up to the n-dimension. The matrix thus becomes a powerful element in the
description of all subatomic physical findings, as well as in the
explanation of the entanglement of dynamic parities, or vibrational
resonances.
The example image in Table 1 shows the rule: Perpendicular to
the center of the 2D triangle at the shortened distance (Pythagorean
theorem), the coordinate Z is the next higher dimension. In this algorithm,
up to 6 dimensions are represented in Table 1.
 Table
1
Table
1
How many dimensions can be described in this way? With mathematics, there is basicly no limit to what can be described. However, the information helps us gain a better understanding of dimensions in general. Our eyes see three dimensions. Our retina, however, only provides two. The impulse in the nerve, however, is only one-dimensional. Dimensionality only affects our intellect. Normally, it is the simultaneous understanding and implementation of three geometric values, which can change causally over time as D4. If we could see four geometric values as simultaneity, we would not need causality. Future and past would actually be merely a fact that slowly blurs at the distance. The effect of time would still appear, but then as a fifth dimension.

Here, n-dimensions are generalized. Mathematics provides us with a surprising amount of information about n-dimensional matrix geometry. Using Pascal's number triangle, the vertices and their relationships (lines) between them can be defined. Table 3 shows us the calculation formula of an n-dimensional coordinate system.

shows the geometric explanation of the following table, showing how an
n-dimensional coordinate system can be calculated.
From these values in n
dimensions (height of the "Dn-tetrahedron"), all other values can be calculated.
The 6 sides of the tetrahedron become the base area of a new pyramid in
D(n+1), whose height = Dn/n. In the transition from
Dn to (Dn+1), the
triangular faces of the tetrahedron are divided into 3 sub-faces (see lower
figures 9; 10; 11), which, with the base area and the specific height hn
from the upper table as Dn/n, again form a tetrahedron, but with optically
shortened lengths. The higher the dimension, the smaller the lengths or
distances of the heights hn
and vertices (OPn), and the greater the number of sub-faces.
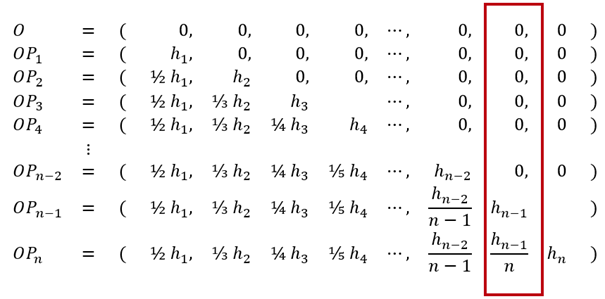 Table 3
Table 3
Here is the coordinate system of the values shown in Figure 8. The dimensional perspective change always happens the same way as D1 to D2 to D3, which is imaginable up to that point. The values hn symbolize the right-angled branch to the center point cp of the dimensional shape Dn. This is the initial value of the closest distance to cp from Dn+1.
With this hexametric coordinate system, all coordinate values can be expressed with integers. Along the new coordinate from (cp), every point on this coordinate is equidistant to all points of the preceding supertetrahedron Dn-1. It is a coordinate system that corresponds to quantum theory. This is, of course, to be expected, since each matrix point corresponds to a quantized energy value. It is the physics of the 21st century that will soon lead us to new, unimagined technologies.
 pix
9
pix
9
In this sense, the hyper-tetrahedron of the fourth dimension has 5 vertices connected by 10 lines.
This representation corresponds to the 2D representation of a tetrahedron
from above as a triangle with lines to the center (the vertex). However,
this is the 3D representation of the "vertex" of the 4D pentahedron, which
takes over the functions of the tetrahedron in the 4th dimension.
The red lines show the edges of the pentahedron, with the
cp (center point)
as the negative pyramid vertex. The height of cp relative to the triangle's
area corresponds to 1/4 of the entire red line in 4D. The result is
multiplied by 1/4 to the formula for the length c4 = cp4√(c3²-(c3/4)²), which
then yields the "height" h4 of the sub-area (negative pyramid) in
4D.
Interestingly, these "heights" become increasingly smaller in the "higher"
(hn+1) dimensions. We must remember that shortenings are only optical. Here,
for example, 3/4 · c4 or 3/4 · 0.817 = 0.6127 (edges of the negative
pyramid)) is the equivalent of 1, the length of the visible dimensions
up to D3.
 pix
10
pix
10
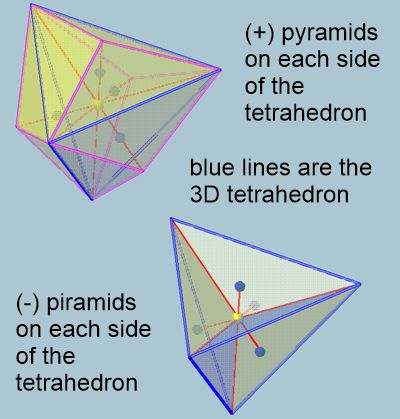
It seems that when considering the n-dimensional geometric shapes of the matrix, a definable freedom of shape change must be taken into account. It is like a breathing of the matrix. The basic assumption that the matrix is a rigid structure must be clarified to say that only the pattern is rigid, but it oscillates internally. The oscillation, however, occurs in the (n+1) dimension, here the negative or positive height of the pyramid above the triangular faces.
In addition to the representation in Figure 9 of a tetrahedron in (-) vibrational parity, there must also be a counterpart, a tetrahedron with (+) curvature of its triangular faces (pyramids), corresponding to the matrix's requirement of equilibrium of all parities, what is the requirement of a stationary medium.
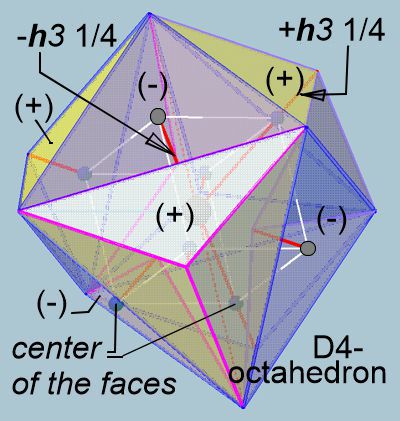 pix
11
pix
11
Since the octahedron is actually just the space between the tetrahedra, it must have the (+) or (-) pyramids on its faces in D3 so that all surrounding tetrahedra fit together perfectly.
The yellowish areas are the (+) pyramids, and the bluish areas are the (-) pyramids. Upon closer inspection, you can see the center of the surface protruding in the bluish areas, while everything is obscured in the yellowish area. This can also be seen when the dark balls (center of the surface) point the red line of h4 /4 = 0.204 outwards or inwards.
A closer look reveals that this height, expressed as an amplitude plus or minus, is larger for the octahedron than for the tetrahedron. This demonstrates that energies from higher dimensions always act toward the center of the octahedron. The energies in D(n+1) space are normally neutralized to zero in the tetrahedra (the scale of the matrix adjusts). However, it appears that specific energy quantities never change, making the lifetime of a proton appear infinite.
Considerations of the dimensions in relation to the MATRIX
 pix 12
pix 12
In isometry, the base of the 2D tetrahedron is divided into three triangles.
These represent 1/3 of the base. However, this is only the isometric
shortening of the true size of the triangles and is only visible in the
third dimension or (Dn+1). This also applies to all other n-dimensions. In the
representation in Figures 10 and 11, it must be realized that the resulting
triangles all have only one size of the 60° base triangle. This principle
applies to all dimensions. Our consciousness must become accustomed to the
fact that everything visible to us only applies to the third dimension. The
true sizes are based only on the first dimension. This applies to the entire
universe. All true sizes of energies are therefore D1 strings, D2 - Dn
effects are simply the sum of these energy strings. They form the units that
determine the matrix scale; in other words, the scale of distances results
from its uniform string sizes (energies).
The following applies: ʎ=h·c/E,
wavelength=Planck constant · speed of light / energy
The heartbeat of our world is a pulsating
moment h=p·ʎ
that is invariant and has a universal magnitude
https://www.michaelis.ch/matrix-2-d.html#oscillation-d
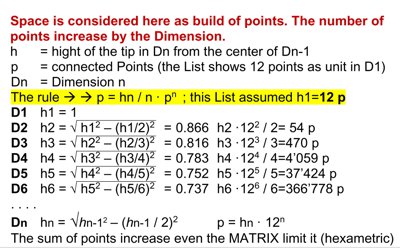 Pix
13
Pix
13
To consider the volume of space in all dimensions, a "point space" is
assumed. This consists of points with equal spacing on all sides, which
geometrically always generates the matrix. But what influence have
dimensions? A point grid in D2 fills a D2 size faster than in D4. The table
shows a size of 12 points in D1. The number of points increases here to
3,66,778 points in D6 with a unit side length of 12 points!!! The distance
between the points mysteriously remains the same.
A theoretical idea: A
journey at 1/3 the speed of light to a star 10 light-years away now takes 42
minutes in D6 instead of 30 years. (Do the math!)
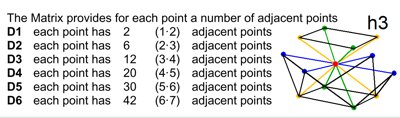 Each point in the matrix is in direct contact with its neighbors. In D1,
there are 2 points, in D3, there are 12, and in D6, there are 42 points. In
the image, it is the red point in D3, which has 12 neighbors: 4 upwards
(60°), 4 horizontally (dark blue), and 4 downwards (60°). They fulfill the
matrix's parity rule. This rule applies in all dimensions. With 42
neighbors, information can be processed much faster than today's digital
computer technology in D1.
Each point in the matrix is in direct contact with its neighbors. In D1,
there are 2 points, in D3, there are 12, and in D6, there are 42 points. In
the image, it is the red point in D3, which has 12 neighbors: 4 upwards
(60°), 4 horizontally (dark blue), and 4 downwards (60°). They fulfill the
matrix's parity rule. This rule applies in all dimensions. With 42
neighbors, information can be processed much faster than today's digital
computer technology in D1.
All energies in the higher dimensions (Dn) are radiation in Dn and are transferred into energy fields that become local in D(n-1). This is because Dn is always perpendicular to the lower dimension D(n-1) and is therefore an oscillation with a perpendicular vector to the action dimension D(n-1). However, since the oscillation parities (+/-) act perpendicular to D(n-1), they only create a compression of space in this dimension (D(n-1), which, according to ʎ=h c/E, results in a local energy field. This explains gravity from energies in D(3+n).
Gravity, however, is an energy field, essentially a multi-field of smaller fields, up to the excitation field unit. These excitations, however, retain their parities and remain as string effects (+/-). It is the momentum on the D(n+1) coordinate that only combines with the effect on the Dn coordinate to form a field effect.
In this sense, the entirety of particle physics can be explained. There, mass and inertia are the D3 effect (fields) of the energies from D(3+n). Particles, however, are the excitations from D(3+1) in D3, whose parity is the charge. Parity and excitation are essentially the same thing; parity belongs more to theory, while excitation belongs to experiment. The effect of setting charge in motion creates charge strings, which have been defined as magnetism.
The multidimensional matrix replaces the old term space
The theory of the matrix described above provides new perspectives for
understanding all these forces. Many phenomena of a new physics, such as
entanglement or vibrational affinity, the
cancellation of gravity, or field phase shifts, can now be
described exactly by including higher dimensions. The direct relationship of
the vibrational moments and their compact pattern in n+1 dimensions causes
phenomena that no longer require space (nonlocality). The
change of state of the fields considered as parities of vibrations makes
rotation as spin and gyrality obsolescent.
With Einstein, it can be said that God does not play dice.
For a deeper understanding of matrix theory, I recommend my other papers.
the Matrix Theory
the Oscillation of the world medium
the medium of space
the universe, peering through the illusion
Friedmann-space and the Matrix-Theory
space-time continuum
space-time as illusion
particle in the Matrix
the Electron
Gunter Michaelis, 22.7.2022 / 4.4.2025
