Field theory derived from the matrix of space
This part is about a quantum-field theory, which is mainly derived from the properties of its medium, the space-time-pulse continuum. The resulting phenomena such as particles, mass / inertia, charge etc. are here new explained.
A particle is no longer a separate field, it is the state of the medium at that location.
From this prospective, no new particles are created in CERN, only the state of the location was manupolated. All forces, all interactions arise from the disturbances of the original oscillation of space, of time (which also oscillates) and of pulse. Instead of mysterious quantum numbers, the states of the location are included in the calculation. There are no more sharp defined location. Everything that is is oscillation, has a different state in every pica-second. Only a constant repetition, a cyclical patterns are what will be recognizable and what counts. The small cycles are the medium of larger ones. There is no beginning, there is no Planck length or the values of time and mass derived from it.
measurable physics doesn't stop where measurability ends..
But it also makes no sense to look for limits where none can be. The concept of a matrix as a polydimensional geometry allows to explain the geometry of standing fields and thus changes many standard interpretations of physics.
Despite a fundamentally rigid determination of the geometric Matrix, at
least one property of the space must be recognized. The degree of freedom
therefore requires an elasticity, a bending potential that allows
deformation and resistance. Only this elasticity creates the moment
h=pulse▪ʎ, a form of energy E=hf (h=Planck constant, λ=wavelength,
f=frequency). Since h is invariable, only λ and f can change in the space
cells. However, the geometry of the Matrix requires that these changes be in
integer ratios. For a deeper understanding look at
field and quantum dynamic)
 blue
fields have the same energy size as the pressed red field (S9)
blue
fields have the same energy size as the pressed red field (S9)
The standing or bound fields around the center of a particle have their own relativistic metric of their rod size (or Comton length ʎ), pulse and frequency. An interaction with other particles always takes place in the same scale. For example, an electron interacts with a proton in S27 to S81 (S=scale, where S1=proton), the field of the elementary charge e=1.602 10-19 coulombs of the SM (standard model), as later in part 4 is explained in detail. The designation e=1eV=1240nm (Comton-λ) will be preferred there.
The standard model (SM) requires the criterion of charge (+) or (-) for the above-mentioned interaction. This is replaced by the MFT (Matrix-Field-Theory) by the term parity, since MFT regards all particles as oscillation, which means a change of (+) and (-). But this requires to give up the empty space theory with the dynamic of separate particles. In MFT, a particle is a modification of space and connected with the whole. Therefore a particle oscillation is always in the same rhythm as its medium, here the location (x; y: z: t.) A particle is therefore not (+) but has in this specific location (x; y; z; t)=(+). No matter where the interaction particle (here the electron) is, it has the same parity ratio everywhere in space.
proton always has opposite parity
of an electron (+/- or -/+) at the point of interaction
Field and scale
The normal concept of
a field in space is a realm of equal or coherent
properties. Its shape and size depend on the scale of its effect (λ=h▪c/E). The medium
connects space and time cells to a network of the same properties. In the
smallest scales of space and time, the order of magnitude of protons,
electrons and neutrinos, shapes are formed from octahedra and tetrahedra. 
On scale of charge fields of electrons (S9 to S81), fields of electrons become preferred locations with a high probability of hitts (electron detection). On the chemical scale but, they become quite round. There, the quanta blur as the sum of many quanta and are perceived as analog quantities. There are several fields with almost identical centers. They result in mixed quantities that consist of quantized individual quantities (E=hF) and total quantities with a distribution E=multiple ΔE/r^2. The geometric shapes become spherical analog shapes on the scale of our environment.
Dynamic and standing local fields
 From
the point of view of space-time, a field has a location and therefore also
time in addition to the momentum. A photon is a propagating field that
changes location with V = c and freezes time within its system. A particle
is a field with the same location but measurable time. The sequences of its
oscillation consist of the radius r (λ) of field and time = r/c.
From
the point of view of space-time, a field has a location and therefore also
time in addition to the momentum. A photon is a propagating field that
changes location with V = c and freezes time within its system. A particle
is a field with the same location but measurable time. The sequences of its
oscillation consist of the radius r (λ) of field and time = r/c.
A photon behaves like a particle when viewed as a single
impulse with the arrow of time pointing left and right. It behaves like a
wave when it interacts or interferes with the parafield
(hyperfield) of the light quantum. These parafields can be very large and
are, in a sense, entangled effects.
Principly everything is now be said about fields. In physics, however, we are primarily concerned with the interaction of fields and this creates further combinations. In short: there are a large number of variant field.
 A
field from a unique multiple occurrence with radially outgoing waves with
amplitudes E=ΔE/r^2, shown here as an area. The z-axis shows the energy of
the amplitude here X;Y; symbolizes the space. Multiple causes (with
multible centers) create an
analog field rather than a quantum field situation.
A
field from a unique multiple occurrence with radially outgoing waves with
amplitudes E=ΔE/r^2, shown here as an area. The z-axis shows the energy of
the amplitude here X;Y; symbolizes the space. Multiple causes (with
multible centers) create an
analog field rather than a quantum field situation.
This consideration only applies to flat space. But since energies in all sizes (scales S1-Sx) diverge completely, the SM creats independent areas of different forces in physics, which are presented as natural forces without deeper connections. The areas of strong and weak nuclear force and EM force are explained in more detail below.
 Here a standing field with its resonance fields. The octahedron in the center is
the primary field. In the case of a proton its size would be S1 and in the
case of an electron S3. Everything is quantized in this order of magnitude.
An interaction would not be E=ΔE/r^2 as by multiple fields, but E=hc/λ, where λ would be the rod length of the field. An interaction only happens
1-dimensionally here. The rods of this size symbolize “strings” of
interaction, its length the time (λ/c). The colors of the points
shown (knots of the material from which space consists) are in Standard
Model the quantum chromo dynamics of virtual particle. Their oscillation changes their colors
per quantum time, but their proportions in the sense of a compensation of
spatial density remain and are carriers of the static image. In the status
of the undisturbed space, the colors are symbol of their state or parity of
oscillation, with
interaction of the "fields", colors and rod lengths and thus also time and
energy are changed. Every field interaction is the game of balancing the
spatial density (or energy in physical terms).
Here a standing field with its resonance fields. The octahedron in the center is
the primary field. In the case of a proton its size would be S1 and in the
case of an electron S3. Everything is quantized in this order of magnitude.
An interaction would not be E=ΔE/r^2 as by multiple fields, but E=hc/λ, where λ would be the rod length of the field. An interaction only happens
1-dimensionally here. The rods of this size symbolize “strings” of
interaction, its length the time (λ/c). The colors of the points
shown (knots of the material from which space consists) are in Standard
Model the quantum chromo dynamics of virtual particle. Their oscillation changes their colors
per quantum time, but their proportions in the sense of a compensation of
spatial density remain and are carriers of the static image. In the status
of the undisturbed space, the colors are symbol of their state or parity of
oscillation, with
interaction of the "fields", colors and rod lengths and thus also time and
energy are changed. Every field interaction is the game of balancing the
spatial density (or energy in physical terms).
All dynamics are caused by this law.
Parity and Interaction
 Here the topic of parity or charge of part 2
will be deepened: charge / parity
Here the topic of parity or charge of part 2
will be deepened: charge / parity
The term parity is a term of oscillation . One aspect of the matrix is
still missing. It is hyperspace or 4D space. This is explained more deeply on the main page
matrix-dimensions
. It is this aspect who creates a stationary field in the medium which has
an elastic impulse propagation of V=c. It's an oscillation perpendicular
to 3D space. It is not hyperspace itself that is dealed here, but it is the
effect in our 3D-space, what is embedded in a higher-level (4D) space.
As a
result, space as a medium loses its last classical property of Euclidean
space, it becomes 4D space. "Time" is a human concept of 4D coordinates and
only serves our limited imagination. The picture above shoes an 4D-Euclidian
space, the double oscillation is hier SPIN 1/2
The space itself can be deformed.
And it will. And with the deformation the space changes density and time. But time is tied to space because it is
part of
oscillation. The oscillation consists of the bending moment Pulse•λ, and the
frequency f. λ=c/f ↔ pulse▪c/f.
However, the deformation energy generates a counter-deformation, so that
equilibrium is restored.
E-deformation = E-counter-deformation = zero
This defines the strength of the transmitted force and relates it to the λ (radius) of space cells and their frequency. The greater the force transmission, the smaller the space cell or λ of the oscillation that forms this space cell. Everything is dominated by the moment h (Planck constant) of the medium. The structure of the Matrix results from an absolute balance of all properties involved. The phenomena of our world result from its disruption. In this way all existences consist of the same space-time, nothing is separate.
The interaction of onion like arranged fields

From a geometric point of view, a stationary field can only be seen as the cause
of an impact from a further dimension. It should be remembered that the
philosophical principle applies that there is no limit to the dimensions,
only a limit to our understanding. The 4th space dimension demonstrably
casts its shadow in our spatial understanding of 3D space.
See here Part 1:
The dimensions
of space,
Part 2:
The new concept of time .
With this in mind, a point field emerges from 4D space with the impact,
which is used as the primary field of a proton and as a scale S1 for further
observations of spatial geometry.
In addition to the proton, the
primary fields of electrons and neutrinos arise. On the way to understanding
particles, only the relationships between protons and electrons are
important. Neutrinos are too close to the energy fluctuation of
surrounding space or to the entropy of space-time. They have no signifciant influence on
proton and electron interactions.
Before to explain the images shown
below, paradigms need to be redefined.
1.) A standing field needs the pulse from
a 4D space ordinate. This is an oscillation, it is energy, a tensor quantity that
acts perpendicular to all 3 coordinates of 3D space. It acts as + and - to
space-density and initialize by this the local 3D-field.
2.) This pulse has no direct geometrical
influence on our world (the 3D space). All influences are indirect and based
to elasticity. The primary field by this pulse is therefore an indirect
quantity that cannot be directly derived from the impact it self. The
formula E=mc^2 is necessary for this reason, since the formula E=h c/λ has
pure 3D values and is only valid in slightly curved space. In this sense, energy E=h▪c/λ
or pulse▪λ▪c/λ
is here the result of the impact and not the impact itself.
3.)
The theoretical aspect mentioned under 2.) is rounded off with the
assumption that 3D space is influenced by shadows of higher dimensions. The
primary field of a particle is created by a 4D-impact, It can
derived by E=hF what is here only a shadow energy. The energy value of a
particle is the indirect result of space-elasticity as the 4D amplitude of its primary
field.
4.) The other fields around the primary
field are the result of 3D space and are referred to here as
resonance fields. Their relationship with one another is quantized
i.e. ΔE=hF/3. The devisor 3 comes
from the fact that also Δλ=λ/3 is equal to the ratio of an
onion field size 3^x, i.e. the next larger resonance field is 3 times larger
(in the upper picture S1 to S3 etc.). A particle therefore presents itself
as a primary field surrounded by resonance fields arranged in the shape of
an onion. It is this what interact between the particles. Not the primary
fields.
5.) All resonance fields are
located in the 3^x scales. They are separated by fields of the scales of
even numbers (S2; S4; S6; etc.). Energies cannot be held in such fields.
Entropy will be quickly restort. An energy range is therefore always a
field with a scale of an odd number, the highest resonances are found in the scale S3; S9;
S27; S81.
6.) All energies
of standing fields in 3D space, usualy considered as particle, are oscillations
with tensor to the 4th dimension. See here Oscillation
instead of a rigid space and Hyperspace resp. Supersymmetry
SUSI in part 2. There are therefore 2 oscillations: one as noted befor from
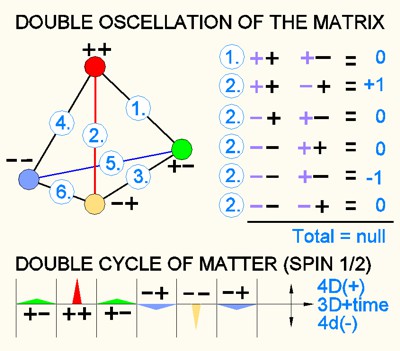
4D and one as primary field in 3D space. Therefor we find 4 parities (++) (+-) (-+) (- -).
7.) In the further consideration, however, the energy states of
(-) time are not used, instead the term parity is added. The proton here has
parity (+), which means that we arbitrarily only consider this part (+) of
the oscillation. An electron therefore always has parity (-) in this
consideration. It would be more correct to say that the electron always has
the opposite parity where it meets a proton.
8.) According to the explanation of particles as oscillation, see
charge / parity
in part 2, standing fields always attract each other.
This is explained by the fact that oscillations are always a vector quantity.
The vectors in the 3D space cancel each other out more or less overall, but
the tensors from 4D space have only one direction (up-down) and can only add up (gravity). Their
secondary fields converge until the amplitudes become too steep. This can be
explained like a mountaineer who has to climb up a mountain and then into an
even deeper valley. After each mountain an even deeper valley appears and an
even steeper mountain. At some point he lacks strength and falls back into
the last valley. When the particles interact, their external fields
penetrate each other until the amplitudes become too steep.
In the diagrams below, the zero line is there the base line, i.e. (+) is red and (-) is blue instead under the zero line. In this way, the example of mountains and valleys could be better presented. However, there are always oscillations, i.e. blue and red changes with the frequency (c/λ).
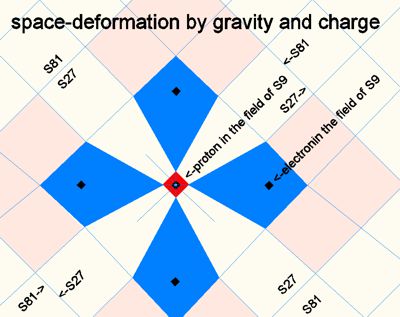
 Blue
is assigned to the electron and red to the proton proton. The charge field
has small centrically arranged sub-fields, which are represented here as
fields with decreasing amplitudes. Since blue and red cancel each other out
at the same location, space is flattened, attraction is created.
Blue
is assigned to the electron and red to the proton proton. The charge field
has small centrically arranged sub-fields, which are represented here as
fields with decreasing amplitudes. Since blue and red cancel each other out
at the same location, space is flattened, attraction is created.
Bottom: The same scenario but with a smaller distance between the
particles. The distance between the centers depends on the local entropy,
i.e. Density of the surrounding space.

Above: Interaction of a proton with an electron. The interference area as a distance is larger here because of opposite parity than with the same parity.
Below: Fields with the same parity also attract each other. However, the energy level of the repelling area is much higher. In case of protons it is the energy level of inside the atomic core.
The Standard Model (SM) allows only for electromagnetics a
+/- attraction, gravity has only attraction. Since not only +/- but also ++ are
subject to attraction in the subatomic area, gluons were invented as a
substitute theory. However, the attitude that space is fundamentally seen as
empty and without a medium also plays a role. Such theoretical ramifications are not allowed in matrix
theory. There is a compaction of space wherever there is mass. It is
generated by the oscillation perpendicular to space coodinates (towards the
center of the 4D sphere). However, this general
attraction of the particles is blocked by secondary fields, which
arrange themselves around each particle (Pauli exclusion). Overcoming these
blocks requires
huge forces, which are normally only assumed in the galactic centers
(nuclear fusion). The protons in the nucleus thus lie in a deep valley where
their neighboring secondary fields overlap.
For a deeper understanding:
The particle fields are
standing fields consisting of the primary field and the centrally arranged
secondary fields. The interaction in the field sizes S10 - S27 is seen here
as electron binding, the charge fields in the EM space. All interactions of
"standing" fields are based on the assumption that the structure of space (its
network) is contracted by tensor oscillations towards 4D-space. Since all
particles are oscillations, there is generally a densification of space, its
entropy, which is thus greater than the zero density of empty space.
Entropy is understood here as the highest degree of uniformity in spatial
density. When the
oscillating vibrations are eliminated (interference or (+) and (-)
combination), this entropy allows the space to be flattend, which causes the
reverse effect of compression. Attraction and
repulsion arise from these two spatial states. Attraction is
therefore the flattening of space (+ / -) = attraction) and repulsion is the
compression of space (+ / +) or (- / -). These space-conditions therefore
replace the term "charge", which cannot oscillate and is
quite an arbitrary interpretation.
The basic forces of physics
 pix
from Wissenschaftsmagazin Scinexx
pix
from Wissenschaftsmagazin Scinexx
The matrix offers an explanation that all basic forces of physics can be
derived directly from the scale of the spatial structure. Basically,
λ=h▪c/E
or λ=h/c▪m
(λ = rodlength)
also applies here, even in SM (standard model) it would only apply to the EM-force.
But the space does not change its basic properties, it is the well-described
EM space in every force range, whose fields in the range of strong nuclear
forces, however, trap the interactions with their steep amplitudes. The influence of the relativistic metric becoms
more relevant, as smaller the scale. It is dependent on the matrix rod length
"λ". Although
referred to as force, these interactions do not correspond to the normal image of the term
"force". They are always an oscillation. You
basically have 2 counterpoints, which always have a distance. But distance
in this small scales is a gauge invariance. The change of distances is
always too an oscillation period, i.e. it has length and frequency what have
to match the space, where this process is happend. Depending on the
arrangement of the attempts at subatomic research and indirect measurement
methods (gauge theory), space deforming energies have the most varied of sizes. Since quantum dynamics only
allows discret values, these values of field deforming were seen in
SM as separate particles. However, the matrix theory sees
these bosons (Glouons, W and Z bosons) as trapped photons in the field of the strong
nuclear force.
The strong nuclear force is responsible for the
chromodynamics in the SM. The quanta are in scale S1. The
matrix geometry and the dynamics of Planck constant create a completely
different picture in the matrix theory. Instead of quarks, the exchange
particles become bosons, in principle photons with a 4D tensor in S1. Only
from S9 onwards can exchange particles be perceived as photons. The
oscillations of the core field S1 create a field with high amplitude /
counter-amplitude that is surrounded by a high Pauli exclusion field.
 Here
briefly: The matrix sees the origin of this force as impulses from 4D space
in the center of the particle (octahedron). The 3 diagonals of the
octahedron create in its direction a chain of same colors. In this sense they are
energy highways. They are considered quarks by the SM. The
matrix theory sees them as flashes of light with a lifespan of about
1o^(-25) seconds and not as particles. It is the interaction within S1 that
only occurs in the case of core destructions in the LHC
(e.g. CERN in Genever). A closer look to the proton crash in LHC,
the kinetik energy pushes the proton deep in the 4D ordinat of 4D-space. The
restoration of the old state goes through various levels of the space
matrix. The discrete bursts of energy released along the 3 diagonals of the
octahedron are then called 3 quarks. These only create an equilibrium
together with the proton itself. charge = p++; Quarks = up+-; down- -; up-+
. Look also here
Charge
Here
briefly: The matrix sees the origin of this force as impulses from 4D space
in the center of the particle (octahedron). The 3 diagonals of the
octahedron create in its direction a chain of same colors. In this sense they are
energy highways. They are considered quarks by the SM. The
matrix theory sees them as flashes of light with a lifespan of about
1o^(-25) seconds and not as particles. It is the interaction within S1 that
only occurs in the case of core destructions in the LHC
(e.g. CERN in Genever). A closer look to the proton crash in LHC,
the kinetik energy pushes the proton deep in the 4D ordinat of 4D-space. The
restoration of the old state goes through various levels of the space
matrix. The discrete bursts of energy released along the 3 diagonals of the
octahedron are then called 3 quarks. These only create an equilibrium
together with the proton itself. charge = p++; Quarks = up+-; down- -; up-+
. Look also here
Charge
The weak nuclear force is in the area S1 to S3 as (Pauli
field), but also in the area S5 to S9 in the
 neutrino
field realm (during the
formation of neutron stars and beta decay). We can see several deviations
from the SM here. However, these depents mainly at the interpretation. The
Matrix has the advantage of a fixed spatial structure, which can be used for
orientation, especially in the area of quantum dynamics. Most of changes
in this realm are in S5, S7 and S9. The interactions there result in a
completely new view of neutrinos. In part 4 it will be explained in more
depth. The picture shows here Protons (p+) and neutrons (n+-). In the scale
S1, a neutron has the same parity like a proton (here red). In S3 but it is
neutral (white). The interaction is happened in S9. The gauge invariance
shoes a dominant space flattening what here means attraction.
Even peaks and troughs in these scale are unimaginal high (EM-space), the gauge
invariance is verry weak.
neutrino
field realm (during the
formation of neutron stars and beta decay). We can see several deviations
from the SM here. However, these depents mainly at the interpretation. The
Matrix has the advantage of a fixed spatial structure, which can be used for
orientation, especially in the area of quantum dynamics. Most of changes
in this realm are in S5, S7 and S9. The interactions there result in a
completely new view of neutrinos. In part 4 it will be explained in more
depth. The picture shows here Protons (p+) and neutrons (n+-). In the scale
S1, a neutron has the same parity like a proton (here red). In S3 but it is
neutral (white). The interaction is happened in S9. The gauge invariance
shoes a dominant space flattening what here means attraction.
Even peaks and troughs in these scale are unimaginal high (EM-space), the gauge
invariance is verry weak.
The electromagnetic force is according to the Matrix theory
basicly and principely in all the ranges of field
 scales. In the SM
(Standard Model) it begins in S9, the next weaker field
region after that of neutrinos. S9 - S27 is the field range (scale) of
electron bonds, the interaction between protons and electrons, which must
have always the same energy level. Because of this, they interact on the same scale
(the elementary charge, it is here in S27 ~ 1eV). The energy quanta are photons. From the point
of view of Matrix space, the energy level for electrons and protons at the
interaction field is the
same, but always has opposite parity.
scales. In the SM
(Standard Model) it begins in S9, the next weaker field
region after that of neutrinos. S9 - S27 is the field range (scale) of
electron bonds, the interaction between protons and electrons, which must
have always the same energy level. Because of this, they interact on the same scale
(the elementary charge, it is here in S27 ~ 1eV). The energy quanta are photons. From the point
of view of Matrix space, the energy level for electrons and protons at the
interaction field is the
same, but always has opposite parity.
The matrix sees the range S81 -
S243 for the chemical bonds of solids. S244 to S729 stands for liquid and
S729 to S2187 for gaseous matter. More are waiting to be discovered
What part does the Planck constant h play in the Matrix?
What is actually h? h =
E/F, it is the pulse energy of an oscillation sequence of frequency F. Since
h is invariant, E and F are proportionally
coherent. h would be the impact here,
which is made compatible to units of energy.
h = E/F ↔ (m▪c^2) ▪ λ/c , ↔ m▪c▪λ.
h = m▪c▪λ ↔ pulse by its rodlength
h is the universal Quant. It is a pulse ▪ λ. Though h is a moment of pulse by
wavelength = p ▪ λ , where λ is the distance of action (sequence) by V=c. This moment is a constance at ground zero of our
physical world. This p▪λ is the ground zero moment h. Theoretically,
this gives us 2 limit values:
1.) m = infinite and λ = zero.
2.) m =
zero and λ = infinite
(this is proof, that our universe must be limited)
Limit value 1: From the point of view of matrix theory, the
value λ of subatomic forces at S1 (the scale of the proton ~
1.3▪10^(-15) m) and the value m at the rest mass of the proton ~ 938 MeV.
Limit value 2: It is probably much smaller than assumed. It
is of the order of magnitude where a quantum effect can no longer be
detected. From then on the quant h=mc▪λ is not recognizable and
the decrease approaches the formula of distribution 1/λ^2 as in case gravity.
The Planck constant is 6.63 10^(-34) J▪s, a value that no one, not even Planck himself, can imagine. It is the impact of a photon with a size of λ=300,000 km. If you consider that a photon of 1 nanometer (1 nm) only has a weak warming effect, then a photon of ~1 meter no longer could have any effect.
Therefore, instead of Planck's giant photon λ=300,000 km, I used a photon of λ=1 nm as a reference, which would then have an effect of 1240 eV. That is a size I can imagine. From this point of view, electrons around the atomic nucleus would be in the size range of S81 = 1240 nm, since the elementary charge = 1eV would be found there. That would be a little help in introducing the size yourself. The interaction of an H atom with the single electron of 13.4 eV would then have the size of λ=1240/13.4=92 nm. This would be ~the smallest distance of the electron location. Finelly Theory becomes Physics.
One could imagine a vibrating construction, which vibrates faster when
compressed (the distance of V=c would be smaller and the number of
kickbacks greater). Conversely, an pulse in cosmic scale (like a huge photon
bigger than a planet) would be on
its own and at some point a
kickback would no longer be
possible. In that point the energy distribution would be E=∆E/λ^2. The impact would
then always have the same size regardless of λ, the distance from the source. Only
a distribution
(E=1/r^2) applies.
We are in the order of magnitude caused by gravity
And here we find the weakest force, gravity, the last fundamental force in physics recognized by the Standard Model. Matrix theory applies the same laws to gravity as to the subatomic fields. However, there is a fundamental difference: The gravitational field is not a phenomenon of 3D space, it is the pure effect of the 4th dimension. The presence of the 4th spatial dimension is explaint in my paper -> MATRIX1 Dimensions .To be clear; our universe is poly-dimensional, of which at least 4 dimensions are needed to explain the Standard Model. The omission of the 4th dimension in physics creates a number of paradoxes and unexplained phenomena. The matrix theory sees space and its fields as 4 dimensional.Time is a shadow of the D4 dimension. Unfortunately, the GFT (General Field Theory) only works with 3 spatial dimensions and separates time.
Here is the explanation why c' as a maximum speed of a n-dimensional
medium always remains the same, even if an n-dimensional freedom of
directions mathematically would the dimensions D1; D2; D3 be significantly
reduce. V=c' only acts in the direction V. The definition of d=V▪t is always
one-dimensional. The other (n-1) dimensions define the start and end points,
but have no quantitative influence on V at this vector. There it applies to
V=c. As we have seen in our cosmological considerations, our universe is
expanding radially from the initial center (Big Bang) with V=c. This is the
same situation as if we were traveling with V=c. All other coordinates D1;
D2; D3 are not affected by 4D relativity because they are perpendicular to
the D4 coordinate. There is no need to increase V=c to V=c·√2 in 3D space.
However, hyperspace is 4 dimensional and there its
relativity in 4D space is c't=√(d1^2+d2^2+d3^2+d4^2), where
is d1= the distance in D1, d2 in D2, etc.
However, that means max. V=c
(in direction of velocity) is valued in all of the dimensions.
To see the picture more clear, we
don´t have the freedom of 4 coordinates as it appears at the first glance.
the 4th dimension is fully occupate by a hyper dynamic and therefore not
anymore in the game of space-dynamics. In this way, Einsteins equation
max V3D
<=ct=√(D1^2+D2^2+D3^2) is still correct in human scales.
Well, how does a gravitational field arise? Only "standing" fields can create a multiple field. They have a resting mass (momentum in 4D) at their center, which in turn causes the secondary fields to form onion like fields around the central primary field. As shown in the chapter Onion Fields , the oscillation towards the 4th dimension creates a general reduction of all field sizes. A field can carry many types of energy, all of which form a vector quantity. They are pulses with uniform direction. However, one type of momentum has a tensor magnitude (not a vector magnitude) in 3D space. This is to be understood in such a way that the size of the pulse itself oscillates, which is equivalent to a vibration of the field strength inwards. While in a multiple field (field cluster) all vectors more or less cancel each other out, tensor quantities of the 4th dimension can only add up. The result in a multiple field (e.g. planet earth) is a significant increase in attraction, commonly known as gravity. In the immediate vicinity of this multiple field, the classic distribution of attraction radially outwards can be seen as F/r2 (force/radius2). Here the field centers are distributed so far in relation to their locations to their weak effects that focusing of all fields as a quantum structure is not recognizable. Even quantum character with respect to the field center still works, but because of so many field centers in an multifield cloud is foggy and not recognizable. This field attracts in all direction except in 4D, where it is called as time.
This is different, however, at a distance of about 1 light year. There
the field cloud (here e.g. earth) becomes a sharply defined point in
relation to the huge distance of 1 light year. The blurriness of the source
locations is no longer effective here. The field structures of 4D-tensors (and
not of the vectors interfering with themselves) become recognizable again.
The Oort cloud will be formed in this way. In further cosmic distances, ever clearer
structures such as the quantum structure of atomic scale can establish
themselves. In this way, interference and culminations of cosmic fields of
large distances (with λ of many light years) will explain many phenomena
that cannot be explained today.
Space is by its quantum effect more bend
as assumed by science. It can´t be explained by the distribution of 1/r^2.
Space has the same distribution in cosmic distances like fields in atomic
small scale. Here an excample: Strings of pearls of stars visible to the
naked eye of a star gazer is good evidence for megastructural effects as
quantum fiel theory.

The world strings
As described above, the ping-pong force h=mc▪λ hardly has any
effect, since the path of the impulse or pulse with V=c is too long and the
frequency becomes less than 1. Since the distance is omitted from the
quantum dynamic formula, E=hf for long distance it becomes then E=h. Here it is referred
to as a pulse. The pulse creates the standing field on a quantum scale. As
described in the previous article, this generates the resonance fields as a
secondary effect of 3D space. For reasons of geometric harmony, these are
always larger in the ratio of 3^x than the next field.
The moderate
puls is actually a multiple pulse effect per unit of time. The
time results from c/λ, i.e. as larger λ, as larger the time interval
between individual pulses and thus as smaller the number of impacts. In
this sense, moderate pulse becomes weaker. In sense of analog physics,
the distance then increases. But even on the scale of quantum theory, the
spherical fields are only probabilities. The physicist speaks of the
collapse of wave function when there is an interaction. Since probability
has no physical reality, the pulse is only a string from its start, but due
to its high oscillation it is seen as a static structure. In quantum theory,
the idea of spherical fields makes sense, as these result in the geometry
of a matrix of always the same field distances. On a larger scale, it makes
sense to see the pulse and also the moderate pulse as a string. As a string,
however, there is no dependence on frequency F and the oscillation wave λ,
only the 2-dimensional energy dilution 1/r^2 applies. It's like with the sea
urchin: the closer to the body of the sea urchin, the denser the spines.
Inside the sea-urchin body we only find a moderate pulse instead of the
spines (single pulse). In the area of the spines we are in the area of
world strings. They still act as a moderate string in the measuring
range of our instruments, but they already have the distribution type of
gravity or E=1/r^2.
The gravitational force then becomes F=G•m/r2. For theorists: The quantum theory would not be violated. Neither does field theory. The wave collapse was described with the one-dimensional formula E=hF. So the string theory also has its explanation. In matrix theory also only 1-dimensional interactions are possible.
Matrix and the illusion of particles

The matrix explains empty space as medium of all physical things. The matrix as a geometric structure of a space of tetrahedral and octahedral is seen from our point of view as nothingness, since its elements, the tetrahedral, are in themselves an equilibrium of all its properties. The sum of its moments is zero. The matrix becomes invisible. The disturbances of this equilibrium in the form of oscillations result in things that make up our world.
Normal disturbances or momenta propagate with V = c through the matrix
structure of our 3D space. They are vector momenta, oscillations, which
change their position by the parity of their oscillation. If the matrix
structure is not recognized, these disturbances are seen as separate
particles.
Physics therefore speaks of photons or bosons instead of
oscillating momenta.
If disturbances are generated by pressure, density and time dilations, they form an anomaly in the centre of octahedrons, which have a 3-color structure, creating the 4th color as a deficit color in there centre. This is a compressed property or moment that can only have a point size effect. But since a point cannot be a vector, this point size becomes a vector to the 4th spatial dimension. As such, it is a local oscillation of the matrix structure. However, if the matrix structure is not recognized and seen only as a void in space, then this local oscillation becomes a separate particle. In addition, the high frequency of the oscillation cannot be recognized either, which means that its parities become special properties of particles. The parities are generated by the 4 color cycle and form a double oscillation between energy densities and (+/-) time. The scale in the matrix creates the energy size of these particles and therefore their type. Further, secondary resonances in 3D space show further properties, which will be described in part 4 of MATRIX4
These particles, the fermions, are seen as separate objects by today's physics, although they are only disturbing momenta in the vibrating matrix structure. For thousands of years of human history, only empty space filled with separate indepented particles has been seen, without realizing that particles are only a disturbance of space (or “nothingness” in their prospect). Physics has reached here the limit of its knowledge. Without the recognition of a structural space-time-pulse mesh, the matrix, no real progress in physics can be expected.
The end of the story gives terrifying results. There are no particles, no emptiness in space and indeed no gaps at all. Our physical universe doesn't really exist as a separate thing. We are only properties of a medium, a reality that can never be directly experienced. We're just the song, not the singer. But this terrible recognition, which breaks our arrogance, also has advantages. If we know the medium, if we recognize the matrix, then we master inertia, space and time. We give our science and physics the chance to explore antigravity and time shifts, things that today's physicist would never dare to think about.
Part 3 tried to give us more tools for looking and understanding at fermions, which will be covered in Part 4. An attempt was made to show a continuous causal line from quantum theory to the scale of our natural analogue environment. It is based on a structure in the smallest detail that is based on space, time and pulse. These 3 terms can only be explained with themselves. They are all invariant at its base. In this way space can be explained with time, time with space. The pulse, however, comes from 4D space, so its size cannot be derived from space and time. At some point in the future the 4D space will also be controllable by us, then only the resistance of the medium, of our univers, the pulse remains as an axiom, left for further explanation.
